MV CIMF Festival

Performance Improvement of Voxel-Based 3D Object Detection Using Distance-Based Selective Sampling
Jihoon You, Injae Lee, Seoneun Kim, Joonki Paik Image Processing and Intelligent System Lab
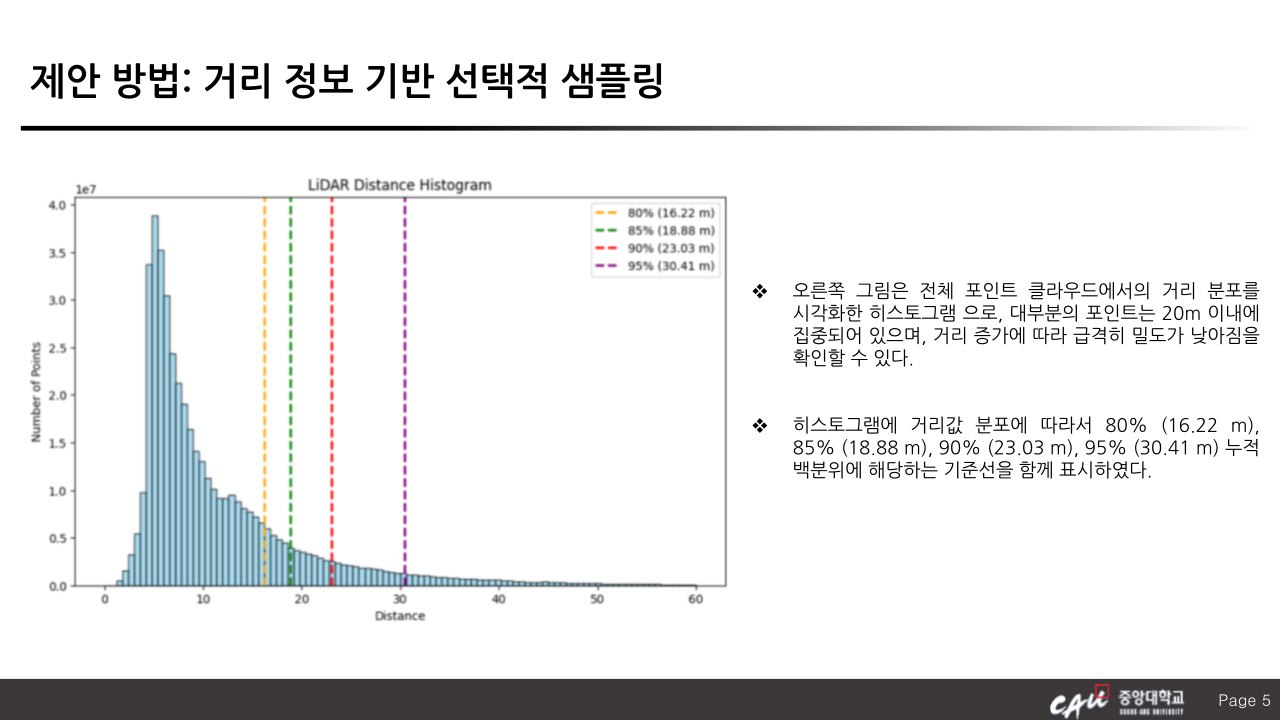
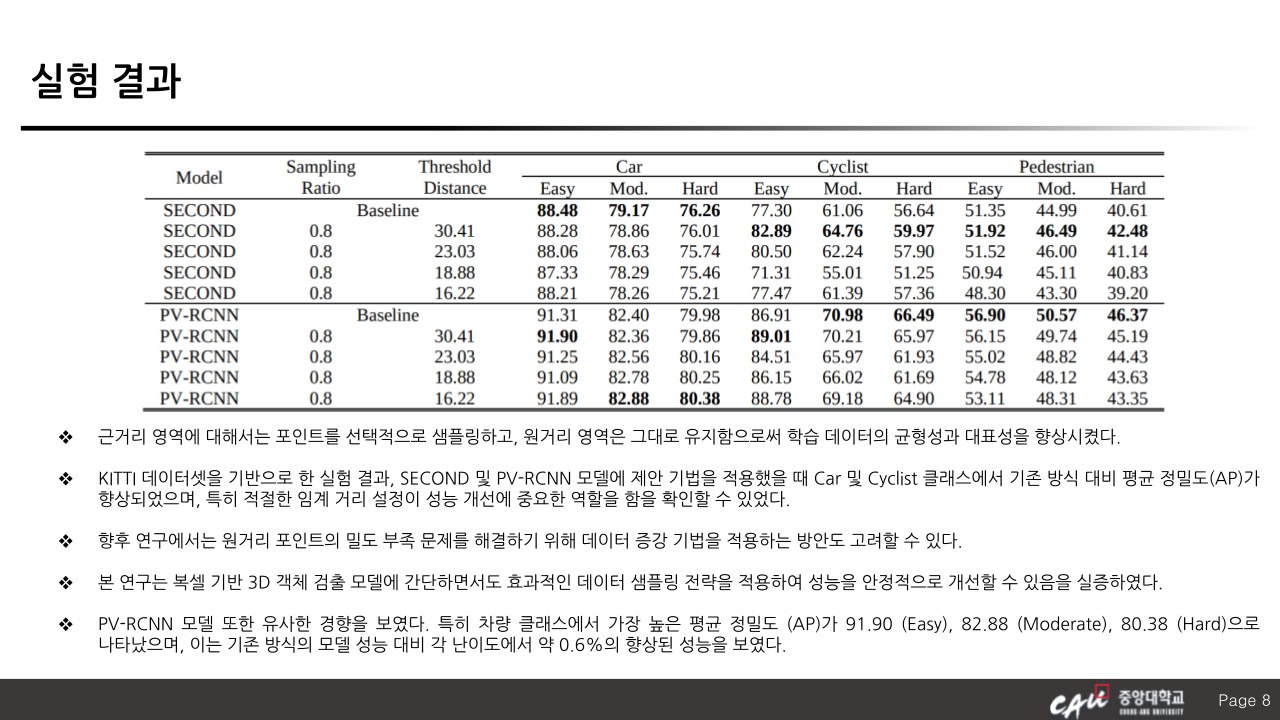
With the increasing demand for autonomous driving and intelligent mobility, 3D object detection using LiDAR sensors has become a key research topic. Voxel-based methods have attracted attention among various approaches due to their regular grid structure and efficient feature extraction capabilities. However, conventional voxel-based detectors still suffer from performance limitations caused by information loss during voxelization and imbalanced point distribution. In particular, point cloud data in distant regions is sparse and low in density, resulting in significantly reduced detection accuracy for far-range objects. This paper presents a Selective Sampling method to enhance voxel-based 3D object detection. The proposed approach selectively focuses on informative regions within voxels by using the spatial distribution and density of points, allowing the network to concentrate its learning on more significant areas. Specifically, point data beyond a certain distance is preserved, while selective sampling is applied to nearer points, effectively mitigating the data imbalance across different distance ranges. This allows for more representative and balanced training data, thereby improving detection performance across the entire scene. The effectiveness of the proposed method is validated through experiments conducted on the KITTI benchmark dataset.